Microsoft recently announced the technical details of the ChromeOS vulnerability they discovered. The announcement states that the company has discovered a memory corruption vulnerability in ChromeOS components that can be triggered remotely, allowing an attacker to perform a denial of service (DoS) attack or, in extreme cases, remote code execution (RCE).
A Microsoft researcher reported the vulnerability to Google in late April of this year.Google assigns it as CVE-2022-2587with a CVSS score of 9.8 (classified as critical) and described as an out-of-bounds write, with a patch released in June.
ChromeOS is an operating system that uses D-Bus. Due to Google’s proprietary hardening measures, there are generally fewer vulnerabilities exposed in ChromeOS than in Windows or MacOS. What Microsoft discovered this time was a ChromeOS-specific memory corruption vulnerability.
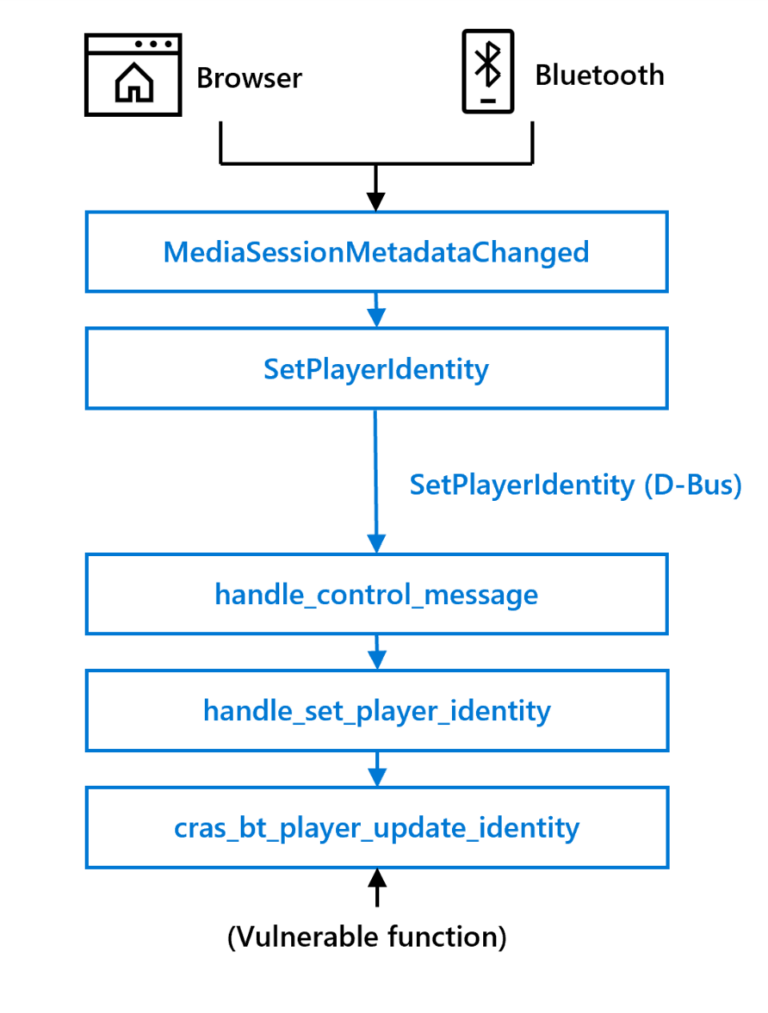
According to the presentation, the vulnerability was discovered in ChromiumOS Audio Server (CRAS); CRAS sits between the operating system and ALSA and is used to route audio to newly connected audio-enabled peripherals. The vulnerability could be triggered remotely by manipulating audio metadata, and attackers could trick users into meeting these conditions, such as by simply playing a new song in the browser or from a paired Bluetooth device, or exploiting adversary-in-the- The middle (AiTM) function exploits the vulnerability remotely.
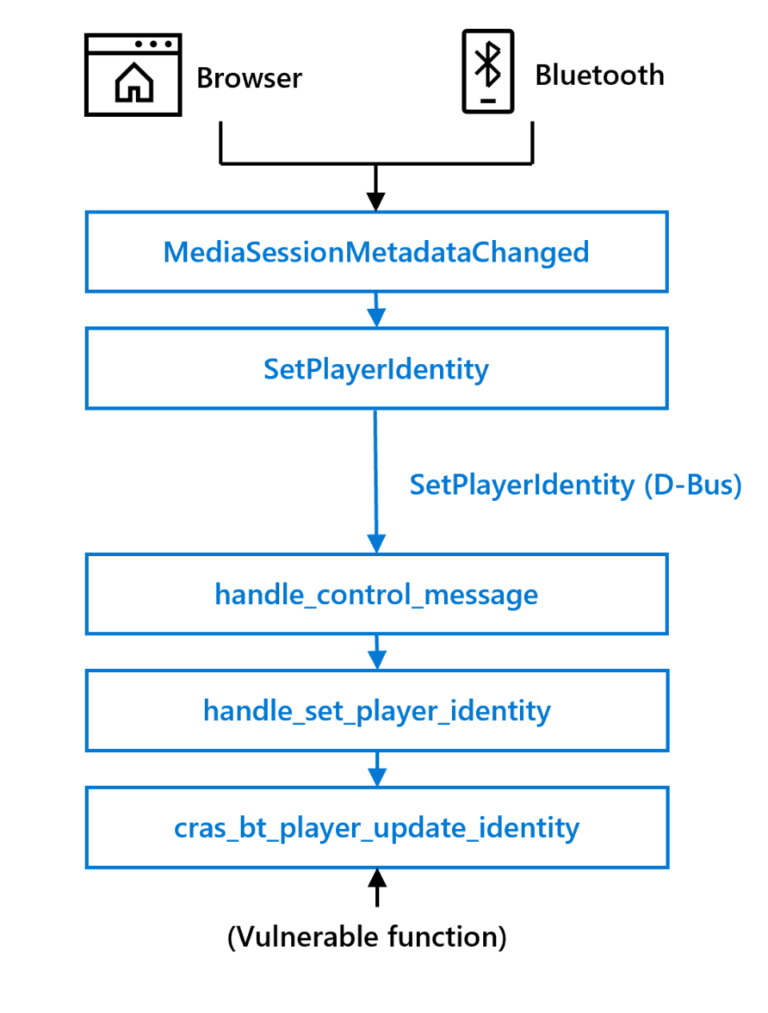
Security researchers examined a handler called SetPlayerIdentity and found that the handler called the C library function strcpy.
“The strcpy function is known to cause various memory corruption vulnerabilities and is considered unsafe because it does not perform any bounds checking. Since the user-supplied identity parameter is not bounds checked before calling strcpy (except for D-Bus messages default message length limit), we are confident that we can trigger a heap-based buffer overflow, which in turn triggers a memory corruption vulnerability. Heap-based buffer overflows can be the cause of multiple vulnerabilities, the most notorious of causing arbitrary Code execution.”
However, Microsoft has not found any signs of the vulnerability being exploited. “The impact of heap-based buffer overflows ranges from simple DoS to full-blown RCE. While it is possible to allocate and free blocks through media metadata manipulation, performing precise heap cleanup in this case is not trivial and an attacker needs to A vulnerability is chained to other vulnerabilities to successfully execute arbitrary code. Given the potential impact of the vulnerability, coupled with the fact that it can be triggered remotely, this is a security risk that justifies vulnerability prioritization and the speed with which fixes are released.”
Microsoft praised Google’s speed in resolving issues after reporting, “We were impressed with the speed of bug fixes and the effectiveness of the entire process. In less than a week, the code was committed and generally available after several merges. Available to users. We thank the Google team and the Chromium community for their efforts to resolve this issue.”
#Microsoft #Reports #ChromeOS #Remote #Memory #Corruption #Vulnerability
Microsoft Reports a ChromeOS Remote Memory Corruption Vulnerability