Android 13 was released more than a month ago, and Google is now actively developing Android 14.latest news,The new version seems to force all devices to use the AV1 codec. Previously, devices only needed to support VP8 and VP9 (the predecessor to AV1), and Google hopes to rely on AV1 to save bandwidth and storage space. Not only that, but some devices using Android 14 also appear to be forced to support 64-bit apps.
AV1 is a royalty-free, efficient video compression algorithm led by the Open Media Alliance, which includes Google, Amazon, Netflix, and more. Google has been a major supporter of AV1, requiring Android TV device makers to support the codec since last year. Currently, Google’s own YouTube platform has AV1-encoded a large number of newly uploaded content in 4K and 8K resolutions. But this content is also encoded using other codecs (mostly VP9) as many devices don’t yet have the capability to decode AV1.
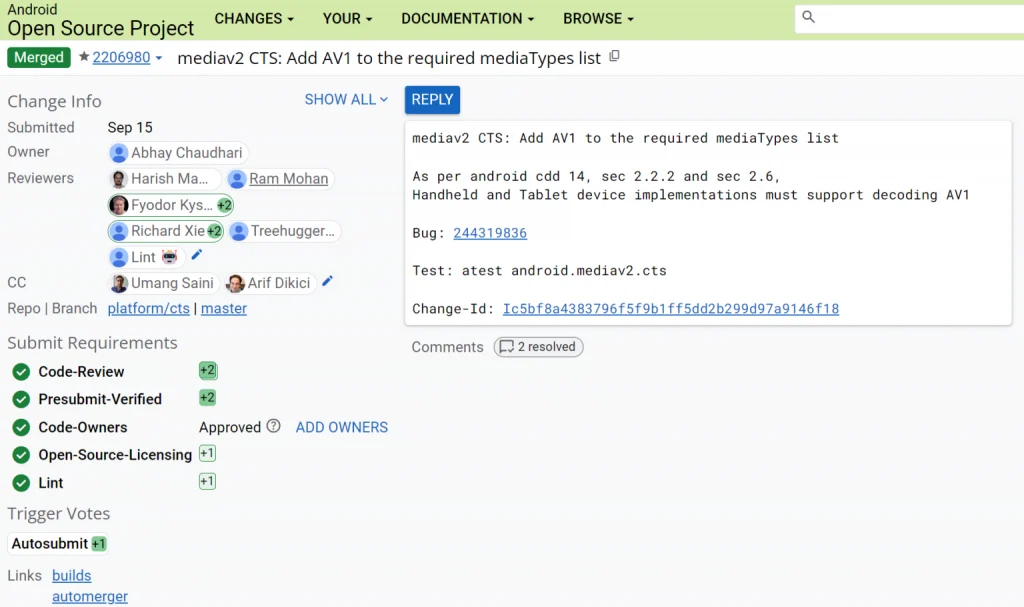
Esper’s Mishaal Rahman shared in his Android 14 preview that the new AV1 requirements are coded in Gerrit, the Android open source project.This requirement has not been reported before, but was recently merged into AOSP Gerrit in a code changehint.The code change is titled“mediav2 CTS: Add AV1 to the list of required mediaTypes”, which is described as “According to Android cdd 14, sec 2.2.2 and sec 2.6, implementations for handheld and tablet devices must support decoding AV1“. It was written by an engineer at Ittiam, the software vendor responsible for uploading many media-related changes to Android, including the platform’s HEVC decoder.
The CDD here refers to the Android Compatibility Definition File, which lists all the requirements a device must meet in order to be certified for an update or release by Google.
Foreign media pointed out that forcing all devices to support AV1 in Android 14 is a big deal, which can reduce the bandwidth requirements of different network services across the platform.
Additionally, there’s one potentially more impactful change for devices using Android 14. Those with Armv9 CPUs will be forced to only support running 64-bit applications. The latest processors are bound to make this switch, and the 2021 Snapdragon 8th generation is already based on the Armv9 architecture. This transition has also begun with the Pixel tablet, which is said to be 64-bit-only at launch.
That means Google is finally getting serious about phasing out 32-bit apps. In fact, Apple has already taken this step back in 2017. Currently, most modern applications have been updated to work on 64-bit architectures, so this change shouldn’t hurt users too much. In fact, 99% of the apps on the Play Store have already been updated. However, this may mean that some old games or apps that have been abandoned by the developers will no longer work.
The official version of Android 14 is expected to be released in April next year.
#Android #force #apps #run #64bit #mode #AV1 #codec #News Fast Delivery