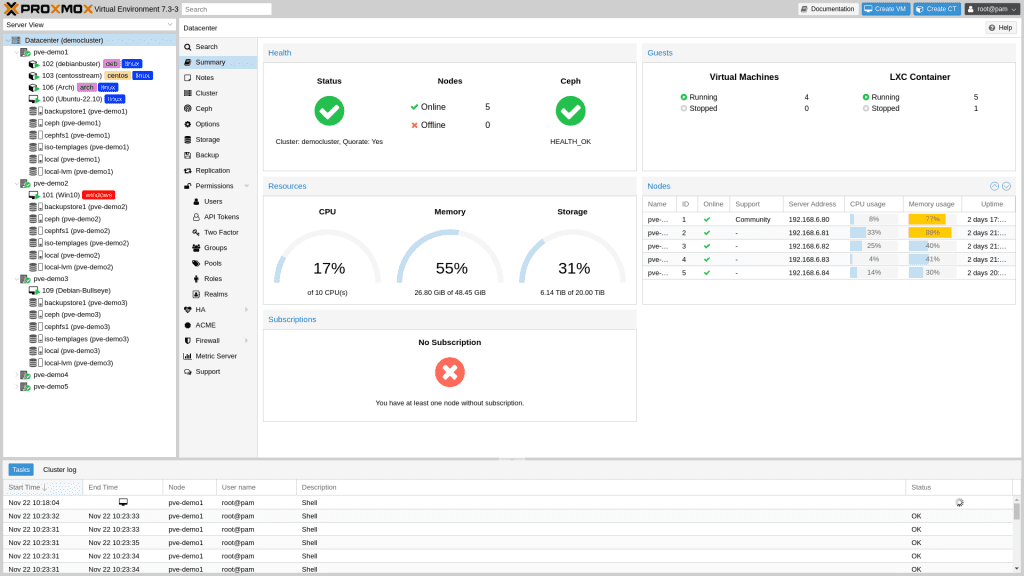
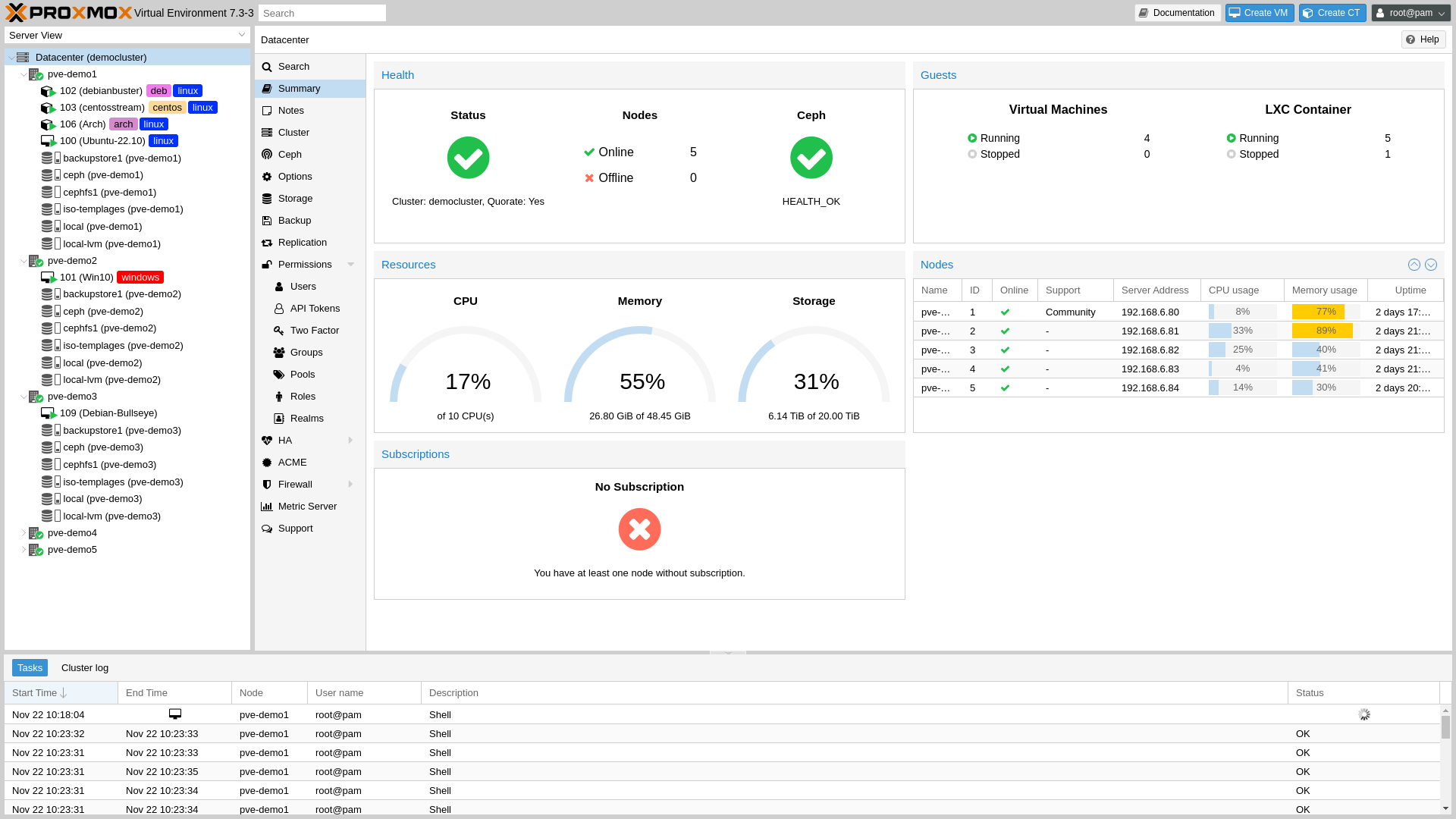
Proxmox VE 7.3 has been officially released.
Proxmox VE (Proxmox Virtual Environment, usually abbreviated as PVE, Proxmox) is an open source server virtualization environment Linux distribution. Proxmox VE is based on Debian, uses a custom Ubuntu-based kernel, includes an installer, a web console, and command-line tools, and provides a REST API to third-party tools. Proxmox VE supports two types of virtualization technologies:Container-based LXC(since version 4.0, version 3.4 and earlier uses OpenVZ technology) andHardware abstraction layer fully virtualized KVM.
Download address: https://www.proxmox.com/en/downloads
Proxmox VE 7.3 is based on Debian 11.5 “Bullseye”, but uses a newer kernel version: Linux kernel 5.15/5.19, and also upgrades important software: QEMU 7.1, LXC 5.0.0 and ZFS 2.1.6.
The most important change in this version is the initial support for Cluster Resource Scheduling (CRS). In cases where Proxmox HA Manager needed to find new host nodes for HA services (e.g. recovery, shutdown policy, HA group configuration changes), it was previously used to count only the number of active HA services for load balancing. This release also integrates the TOPSIS (Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution) method, a multi-criteria decision analysis for finding the best alternative target nodes.
Other changes include:
- Updates to air-gapped systems are enabled through the new Proxmox offline mirroring tool
- Improved user experience for multiple task management features
- Introducing a New Storage Technology: ZFS dRAID
- Support for tagging virtual guests in the web interface
- Introducing new container templates: Fedora, Ubuntu, Alma Linux, Rocky Linux
- Redesigned USB devices: now supports hotplugging
- Proxmox Mobile: Based on Flutter 3.0
- Other enhancements and bug fixes
- …
Detailed update instructions view Release Notes and annouce.
#Proxmox #officially #released #open #source #server #virtualization #management #platform #News Fast Delivery