Version 15.0 of the Unicode Standard is now available, including the core specification, annexes, and data files. This version adds 4489 characters, bringing the total to 149186 characters. These additions include two new scripts for a total of 161 scripts. In addition, this release has 20 new emoji characters and 4193 CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean) ideograms.
New scripts and characters in version 15.0 add support for modern language groups, including:
- Nag Mundari, a modern script for writing Mundari, a language spoken in India.
- A Kannada character used to write Konkani, Awadhi and Havyaka Kannada in India.
- Kaktovik Numerals, designed by the Inupiaks of Kaktovik, Alaska, for the counting system in Inuit and Yupik
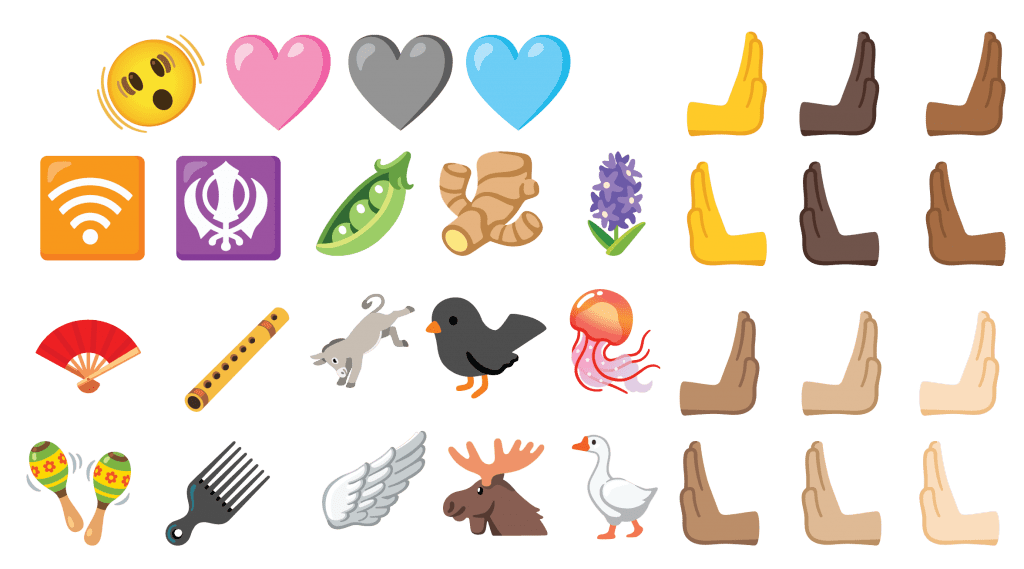
Added 20 new emojis, including goose, flute, folding fan, ginger, pea, pink heart, donkey, jellyfish, and more.
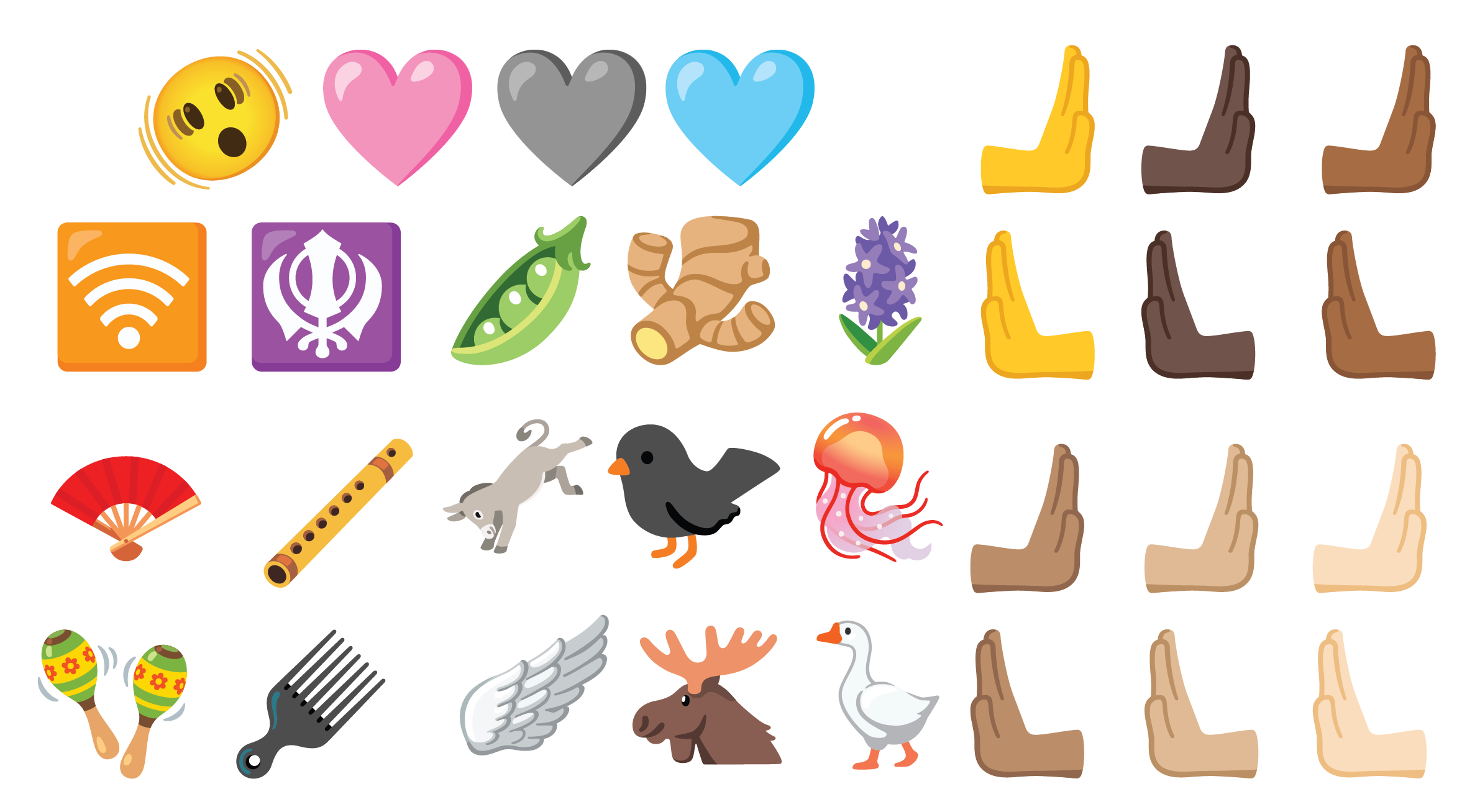
For a complete list of new emoji characters, see Emoji for Unicode 15.0.
Other symbols and additions in Unicode version 15.0 include:
Support for language and academic work includes:
- Kawi, a historical script found in Southeast Asia used to write Old Javanese and other languages
- Three additional characters for the Arabic script to support the Quranic notation used in Turkey
- Three Khojki characters found in handwritten and printed documents
- Ten Sanskrit characters for auspicious symbols in inscriptions and manuscripts
- Six Latin letters used in Malayalam transliteration
- 63 Cyrillic modifiers used in phonetic transcription
Important chart font updates include:
- A set of updated glyphs for Egyptian hieroglyphs, and a standardized sequence of changes to support rotated glyphs in text
- Improved glyphs for unifying Canadian Aboriginal syllables, better support for operators and other languages
- A new Wancho font with improved and simplified shapes
An update to the CJK (CJK) block adds:
- New CJK Unified Ideographs Expand 4192 Ideographs in H-Block
- CJK Unified Ideograph expands an ideograph in a C block
The following six Unicode standard annexes and technical standards were updated in version 15.0 (Unicode properties and specifications determine how text behaves on computers and mobile phones.):
- UAX #9, The Unicode Bidirectional Algorithm, modifies the comments in UAX9-C2 to emphasize the use of higher-level protocols to mitigate potential source code spoofing attacks.
- UAX #31, Unicode Identifiers and Pattern Syntax, provides more guidance for configuration files for default identifiers, clarifies the use of default-ignorable code points in identifiers, and discusses Pattern_White_Space and bidirectional ordering issues in programming languages relationship between.
- UAX #38, Unicode Han database, added kAlternateTotalStrokes property. Changed category of kCihaiT attribute to dictionary index, extended kKangXi attribute, and added sections 3.0, 3.10, and 4.5.
- UTS #39, Unicode Security Mechanisms, changed the zero-width joiner (ZWJ) and zero-width nonjoiner (ZWNJ) characters from Identifier_Status=Allowed to Identifier_Status=Restricted; therefore, the Universal Security Profile no longer allows them by default .
- UAX #45, U-Source Ideographs, documented new ideographs in their data files, added “ExtH” as a new state, improved state identifiers for existing CJK Unified Ideographs blocks, and added section 2.5 .
- UTS #46, Unicode IDNA Compatibility Handling, clarified edge cases for empty tags in ToASCII, and added documentation for new IDNA derived attribute data files.
The Unicode standard is the foundation of all modern software and communications around the world, including operating systems, browsers, laptops and smartphones, as well as the Internet and the Web (URL, HTML, XML, CSS, JSON, etc.). The Unicode Standard, its related standards and data form the basis of the CLDR and ICU versions.
See the release announcement for more details.
#Unicode #standard #released #adding #emoji #goose #ginger #donkey #pea #News Fast Delivery
